Video Outside The Viewport: Google Search Console Returning ‘Video Page Indexing Issue’

In the bustling digital marketplace, the challenge isn’t just to capture viewers’ eyes—it’s to keep them engaged even when they’re not directly looking. Enter the intriguing concept of “video outside the viewport,” a strategy that transcends traditional boundaries of video content. This method involves playing videos in a manner that doesn’t require the user to be directly viewing the video area on their screen, promising a dynamic shift in how content reaches its audience, even beyond the visible frame.
What is “Video Outside the Viewport”?
In the digital world, where visual content often takes center stage, understanding how a video interacts with a web page is crucial for providing a seamless user experience. “Video outside the viewport” refers to a video element on a webpage that is not immediately visible to a user when they first load the page. Instead, the video resides off-screen and requires the user to scroll or navigate to it. This concept is vital in web design and development, impacting user engagement, page load times, and overall interaction dynamics.
Journey into the Digital Frame
Imagine you’ve landed on a website looking for information or entertainment. As you scroll, you encounter various elements—text, images, and perhaps, hidden among these, a video. This video, however, isn’t immediately visible; it exists outside of your current visual frame, or “viewport.” The viewport is essentially the portion of a webpage that is visible to you without needing to manipulate the page’s position. Videos placed outside this visible area can be strategically used to engage users deeper into the content or to manage the pacing of how information is presented.
Why Place Videos Outside the Viewport?
Designers and developers might position videos outside the visible area for several reasons. It can help in:
- Enhancing Loading Speeds: By delaying the load of heavy content like video until needed, the initial page load is quicker, improving the user’s experience.
- Creating Interactive Narratives: As users scroll, they can uncover videos that enhance storytelling, making the experience more engaging and interactive.
- Controlling Resource Usage: This technique can also help manage bandwidth and processing resources, especially on devices with limited capabilities.
Ideo Outside the Viewport: Issues with Size – Too Small, Too Big
Navigating the challenges of video sizing on webpages is crucial for maintaining an optimal user experience. When videos are either too small or too large, it can significantly impact how users interact with and perceive the content. Let’s delve into the implications of these sizing issues and how they can be managed effectively.
The Dilemma of a Video Being Too Small
A video that appears too small on a webpage can easily be overlooked or may fail to convey its message effectively. Users may struggle to engage with the content, missing out on important visuals or text displayed within the video. This sizing issue can be particularly problematic on mobile devices, where screen real estate is limited, and every pixel counts.
To address this, developers can employ responsive design techniques ensuring that the video scales appropriately across different devices. Media queries in CSS, for instance, allow videos to adapt to various screen sizes, improving visibility without requiring user intervention. Moreover, providing controls to expand the video or view it in fullscreen mode can help enhance user engagement.
The Problem with Videos Being Too Large
Conversely, a video that dominates the viewport can be just as detrimental. Large videos can overwhelm other content on the page, distract from the main message, or slow down page loading times, particularly if the video starts playing automatically. This not only affects user retention but can also be frustrating for users with limited bandwidth or slower internet connections.
Optimizing video size and placement involves a careful balance. It’s important to ensure that the video is large enough to be engaging but not so large that it detracts from the overall user experience. Techniques such as lazy loading, where a video only loads when it’s about to enter the viewport, can mitigate performance issues while maintaining visual impact.
Best Practices for Video Placement and Size
- Responsive Design: Ensure videos are responsive and adapt to different screen sizes and orientations.
- User Controls: Provide users with the ability to control video playback, including resizing options if needed.
- Testing Across Devices: Regularly test video playback on various devices and browsers to ensure consistency in user experience.
- Balancing Act: Strategically place videos within the content flow to enhance, not hinder, the storytelling or informational goal of the webpage.
Google Search Console Video Indexing Report
As videos continue to dominate the digital landscape, ensuring they are properly indexed by search engines is paramount. The Google Search Console Video Indexing Report is an essential tool for webmasters and SEO professionals. It provides insights into how well your videos are being indexed and surfaced in Google search results, enabling you to optimize your video content effectively.
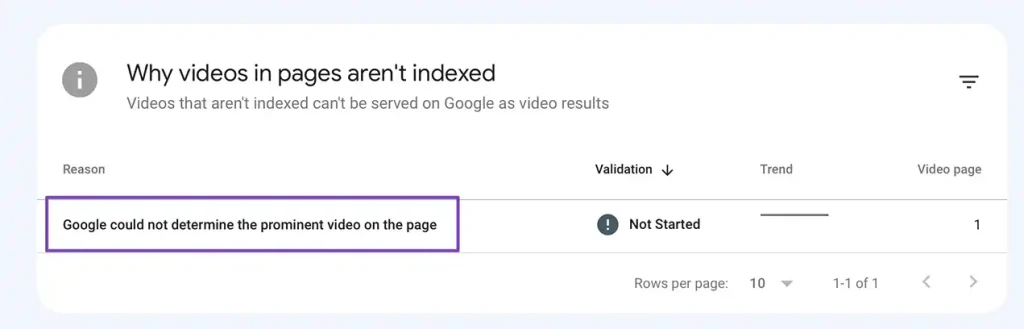
Understanding the Video Indexing Report
Google Search Console offers a specific report known as the Video Indexing Report. This tool is designed to help website owners understand which videos on their site are indexed by Google, which ones are not, and the reasons behind any indexing issues. By using this report, you can:
- Track Visibility: See how many of your videos have been indexed by Google.
- Identify Errors: Learn about any problems that might prevent a video from being indexed, such as accessibility issues or blocked resources.
- Monitor Performance: Check how videos are performing in terms of visibility and user engagement.
How to Leverage the Video Indexing Report for Optimal Performance
- Regular Checks: Make it a routine to check the Video Indexing Report to catch and resolve indexing issues early.
- Resolve Errors: Use the detailed information provided to understand and fix the errors. For instance, if a video is marked as ‘blocked by robots.txt,’ updating the file might resolve the issue.
- Optimize Based on Insights: The report might suggest enhancements, like improving video titles, descriptions, or adding structured data, to enhance visibility.
Real-World Applications
Imagine you have a website dedicated to educational tutorials. By utilizing the Video Indexing Report, you can ensure that your instructional videos are correctly indexed, which is crucial for reaching your target audience. If a key video tutorial on a popular subject like “Python programming for beginners” isn’t indexed, it won’t appear in search results, significantly reducing its visibility and potential impact.
The report also allows you to track changes over time, giving you a clear view of how adjustments in your video strategy impact visibility. Whether you’re dealing with technical SEO for videos or striving to enhance user engagement, the Video Indexing Report becomes a critical tool in your arsenal.
Next Steps in Video SEO
Using the insights from the Video Indexing Report, you can strategically plan further content, optimize existing videos, and adjust your video marketing strategies to better meet the needs of your audience and the requirements of search engines. This proactive approach ensures your content remains competitive and visible, driving more traffic and engagement to your site.
Video Outside the Viewport: 3 Possible Solutions
When videos are not immediately visible within the user’s viewport, it poses unique challenges for engagement and performance. However, this common issue can be effectively managed with strategic solutions. Here are three practical approaches to ensure that videos outside the viewport contribute positively to user experience and site performance.
1. Lazy Loading Implementation
Lazy loading is a technique that delays the loading of non-critical resources at page load time. Instead, these resources are loaded at the moment they are needed, which is when they enter the viewport. Implementing lazy loading for videos can significantly enhance page load times, conserve bandwidth, and reduce initial load strain on server resources.
- How to Implement: Use HTML5 or JavaScript to defer loading of videos until they are about to enter the viewport. This can be done by placing a placeholder image or a lightweight preview of the video, which is replaced by the actual video when the user scrolls near it.
2. Optimal Video Placement
Strategic placement of videos on the page can ensure they catch the user’s attention at the right moment. Positioning a video just below the fold, for example, can pique curiosity and encourage users to scroll down to view the video, increasing engagement and time on page.
- How to Implement: Conduct A/B testing to determine the most effective placement of videos on your pages. Analyze user behavior to see where users typically begin to disengage and place videos accordingly to regain their attention.
3. Thumbnail Quality and Appeal
Enhancing the appeal of the video thumbnail can also play a significant role in enticing users to scroll and discover videos outside their initial viewport. A compelling thumbnail acts as a visual cue that something valuable lies ahead, encouraging further interaction.
- How to Implement: Design high-quality, engaging thumbnails that accurately represent the video content. Use eye-catching images and include overlays of key information or captions that promise value, making it irresistible for users to scroll and find out more.
Balancing Performance and Engagement
By integrating these solutions, you can balance performance with user engagement. Lazy loading optimizes performance, optimal placement boosts engagement, and attractive thumbnails draw attention to the video content. Each strategy has its merits and can be adapted based on the specific goals and layout of your website.
Practical Example
Consider a website that features cooking tutorials. By implementing lazy loading, the site ensures videos do not affect the initial page load, allowing users to browse recipes quickly. Placing an engaging video thumbnail just below the fold, accompanied by a tempting caption like “Watch our quick tutorial on making the perfect soufflé,” encourages users to scroll down, thus increasing engagement and providing value through visual learning.
Conclusion
In the digital age, video content is king, but its impact depends significantly on strategic placement and optimization. Videos placed outside the viewport can challenge user engagement and site performance, yet, when managed correctly, they offer unique opportunities for enhancing user experiences. By employing techniques such as lazy loading, optimizing video placement, and improving thumbnail quality, websites can effectively draw users into deeper interaction while maintaining optimal performance.
These strategies ensure that videos contribute positively to the narrative and purpose of your site, regardless of their initial placement. The implementation of lazy loading not only speeds up page loads but also conserves bandwidth, making your site more accessible and user-friendly. Thoughtful video placement and compelling thumbnails can significantly boost user engagement, encouraging visitors to explore your content further.
